The cellranger vdj pipeline can be used to analyze 5' Single Cell V(D)J libraries. It takes FASTQ files for V(D)J libraries and performs sequence assembly and paired clonotype calling. The pipeline uses the Chromium Cell Barcodes (also called 10x Barcodes) and UMIs to assemble V(D)J transcripts per cell. Clonotypes and CDR3 sequences are output as a .vloupe file which can be loaded into Loupe V(D)J Browser. Visit the What is Cell Ranger page to learn more about Cell Ranger for Immune Profiling.
This page provides an overview of the cellranger vdj algorithm. Click on the sections below to learn more about each step.
Algorithm overview
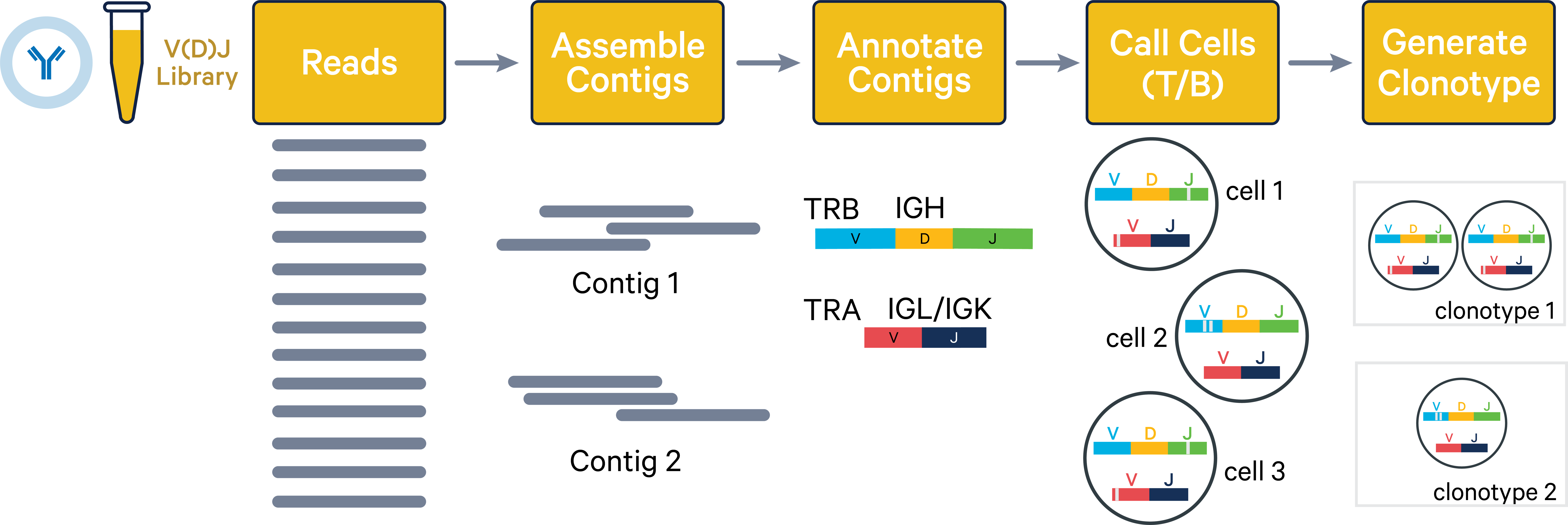
The assembly process combines reads for a single barcode into assembled contigs, representing the best estimate of the transcript sequences present. Learn about the assembly algorithm here
- Filter out reads with noisy barcodes and UMIs that may arise from PCR errors, sequencing errors, etc.
- Trim adaptors and primer sequences from 5' and 3' ends of the reads.
- Generate full-length transcripts (contigs) from each chain in all observed GEMs/barcodes.
V(D)J contig annotation involves aligning V, D, and J gene segments to contigs, identifying CDR3 sequences, and assessing whether each contig is productive, indicating a likely functional T or B cell receptor. Learn about the assembly algorithm here
- Annotate contigs with V(D)J segment labels and locate CDR3 regions that form the transcript.
- Filter contigs that are full-length and productive.
Identify barcodes/GEMs that contain T or B cells. Learn about the assembly algorithm here
Group cell-associated barcodes into clonotypes and filter out some cells. Learn about the assembly algorithm here