The cellranger vdj pipeline can be used to analyze sequencing data produced from Chromium Single Cell 5' V(D)J libraries. It takes FASTQ files from V(D)J libraries and performs sequence assembly and paired clonotype calling. It uses the Chromium cellular barcodes and UMIs to assemble V(D)J transcripts per cell. Clonotypes and CDR3 sequences are output as a .vloupe file which can be loaded into Loupe V(D)J Browser.
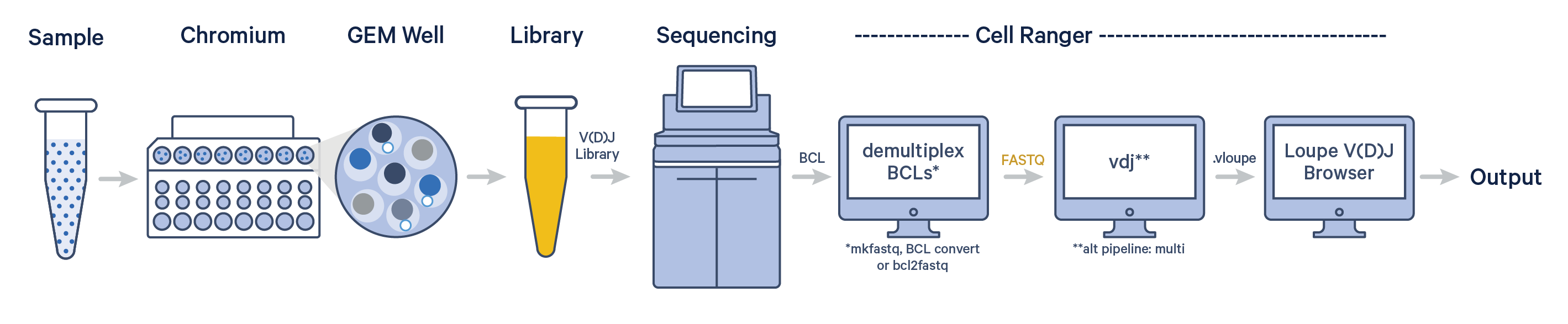
To generate FASTQ files, use one of Illumina's demultiplexing software. For help getting started, try the cellranger vdj tutorial.
For a complete list of cellranger vdj command-line arguments, run cellranger vdj --help or visit the Cell Ranger Commands page.
To generate single cell V(D)J sequences and annotations for a single library, run cellranger vdj with these required arguments:
| Argument | Description |
|---|---|
--id | Required. A unique run ID string: e.g. sample345 |
--fastqs | Required. Path of the FASTQ folder, e.g., /home/jdoe/runs/HAWT7ADXX/outs/fastq_path. Can take multiple comma-separated paths, which is helpful if the same library was sequenced on multiple flowcells. Doing this will treat all reads from the library, across flowcells, as one sample. |
--reference | Required. Path to the Cell Ranger V(D)J compatible reference e.g. /opt/refdata-cellranger-vdj-GRCh38-alts-ensembl-7.1.0. If --denovo is specified, this parameter is optional. |
--sample | Required. Sample name as specified in the sample sheet supplied to the dumultiplexing software. Can take multiple comma-separated values, which is helpful if the sample was sequenced on multiple flowcells and the sample name used (and therefore fastq file prefix) is not identical between them. Doing this will treat all reads from the library, across flowcells, as one sample. |
For help on which arguments to use to target a particular set of FASTQs, consult Specifying Input FASTQ Files for cellranger count and vdj
After determining your input arguments and options, run cellranger vdj:
cd /home/jdoe/runs
cellranger vdj --id=sample345 \
--reference=/opt/refdata-cellranger-vdj-GRCh38-alts-ensembl-7.1.0 \
--fastqs=/home/jdoe/runs/HAWT7ADXX/outs/fastq_path \
--sample=mysample \
--localcores=8 \
--localmem=64
Following a set of preflight checks to validate input arguments, cellranger vdj pipeline stages will begin to run:
Martian Runtime - v4.0.8
Running preflight checks (please wait)...
yyyy-mm-dd hh:mm:ss [runtime] (ready) ID.sample345.SC_VDJ_ASSEMBLER_CS.VDJ_PREFLIGHT
yyyy-mm-dd hh:mm:ss [runtime] (run:local) ID.sample345.SC_VDJ_ASSEMBLER_CS.VDJ_PREFLIGHT.fork0.chnk0.main
yyyy-mm-dd hh:mm:ss [runtime] (ready) ID.sample345.SC_VDJ_ASSEMBLER_CS.VDJ_PREFLIGHT_LOCAL
...
By default, Cell Ranger uses all available system cores. To specify a different number of cores, use the --localcores option (e.g., --localcores=16 limits usage to sixteen cores). Control the memory allocation with --localmem, specifying the limit in gigabytes (GB).
For a complete listing of the arguments accepted, visit he Command Line Argument Reference page, or run cellranger count --help.
A successful cellranger vdj run should conclude with a message similar to this:
Waiting 6 seconds for UI to do final refresh.
Pipestance completed successfully!
The output folder name is the same as the sample ID you specified (e.g. sample345). The outs subfolder contains the main pipeline output files.
Once cellranger vdj has successfully completed, you can browse the resulting summary HTML file in any supported web browser, open the .vloupe file in Loupe V(D)J Browser, or refer to the Understanding Output section to explore the data by hand.