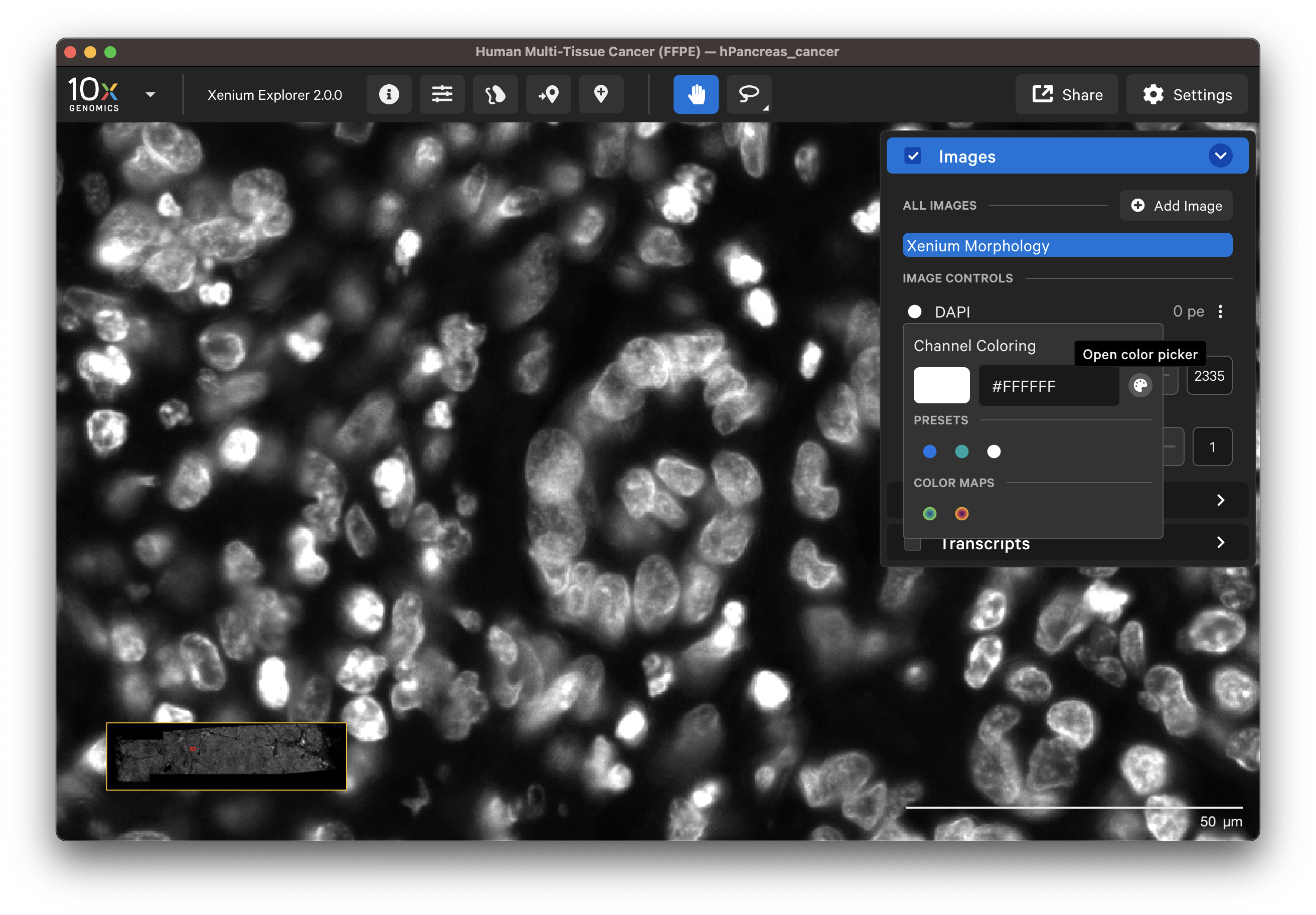
The Xenium Analyzer captures vertical stacks of images every cycle and in every channel for multiple fields of view. The stacks are processed and stitched together to build a single image of the tissue section. Xenium Explorer displays the X-Y dimensions of the image. The Image options panel allows you to explore the Z-dimension. The zoom slider controls zooming in/out on the image. All data in the main Xenium Explorer window can be rotated in 90 degree increments by clicking the Rotate Image button (Per-Gene Localization images cannot be rotated at this time).
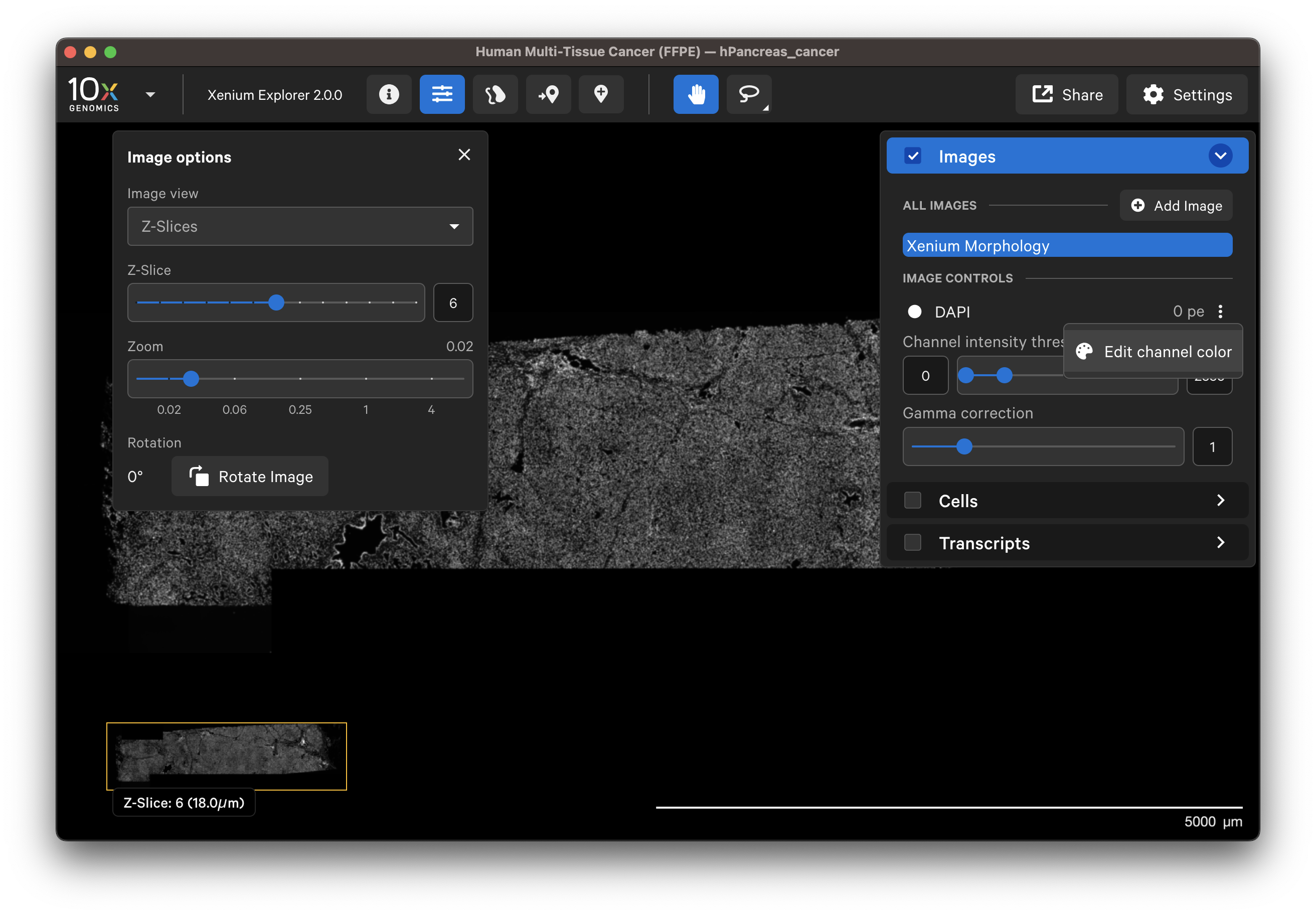
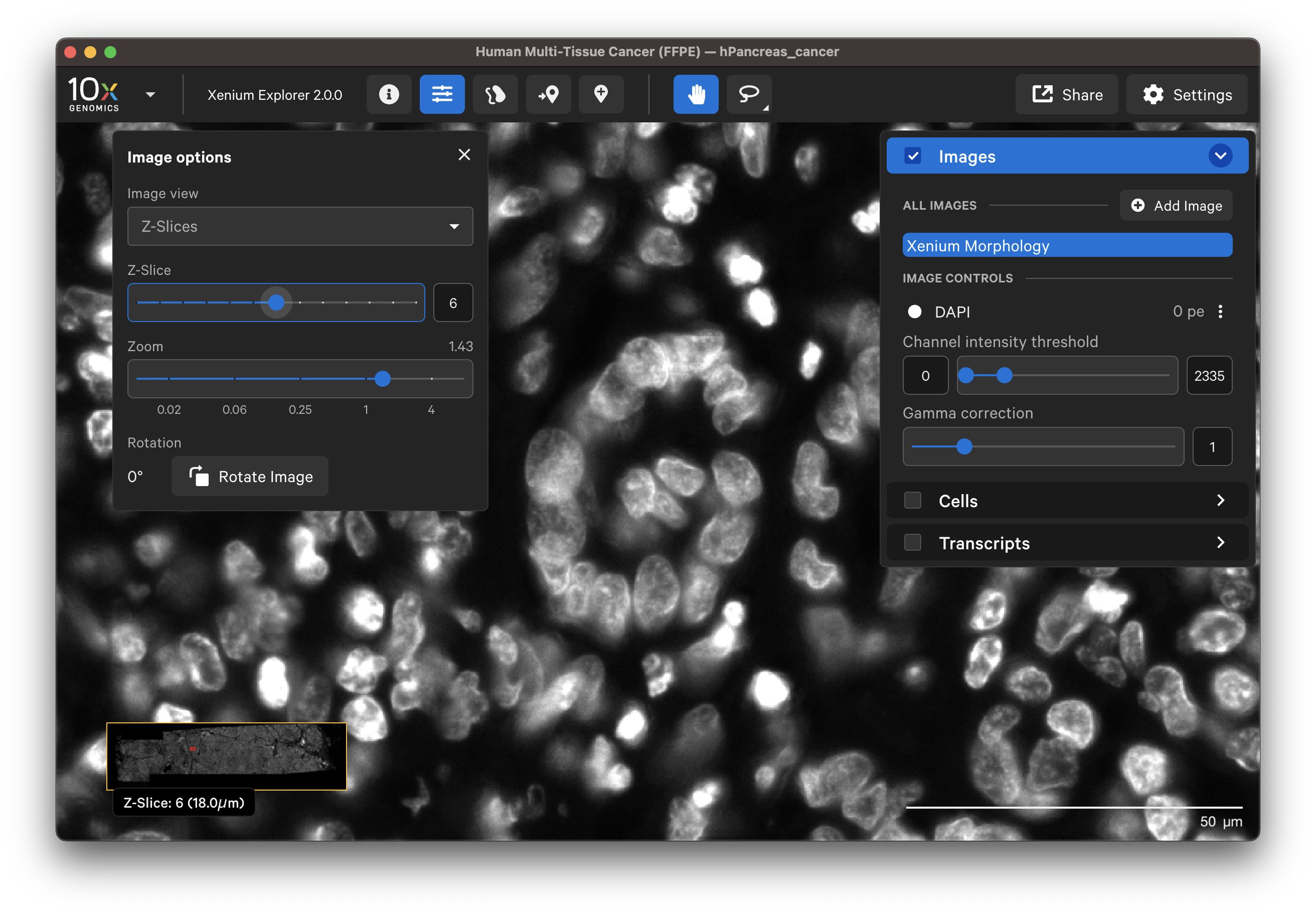
When Z-Slices is selected as the image view, you can view the 3D DAPI morphology.ome.tif tissue images from different Z-plane depths. The Z-slice depth in µm is shown in the lower left-hand corner. Zoom in to a region of the image, and click through different Z-slices. The nuclei should look fuzzy, come into focus, and then go out of focus again as you sweep through the Z-plane of that region of the tissue. This feature can be useful for examining cell structure within the tissue volume.
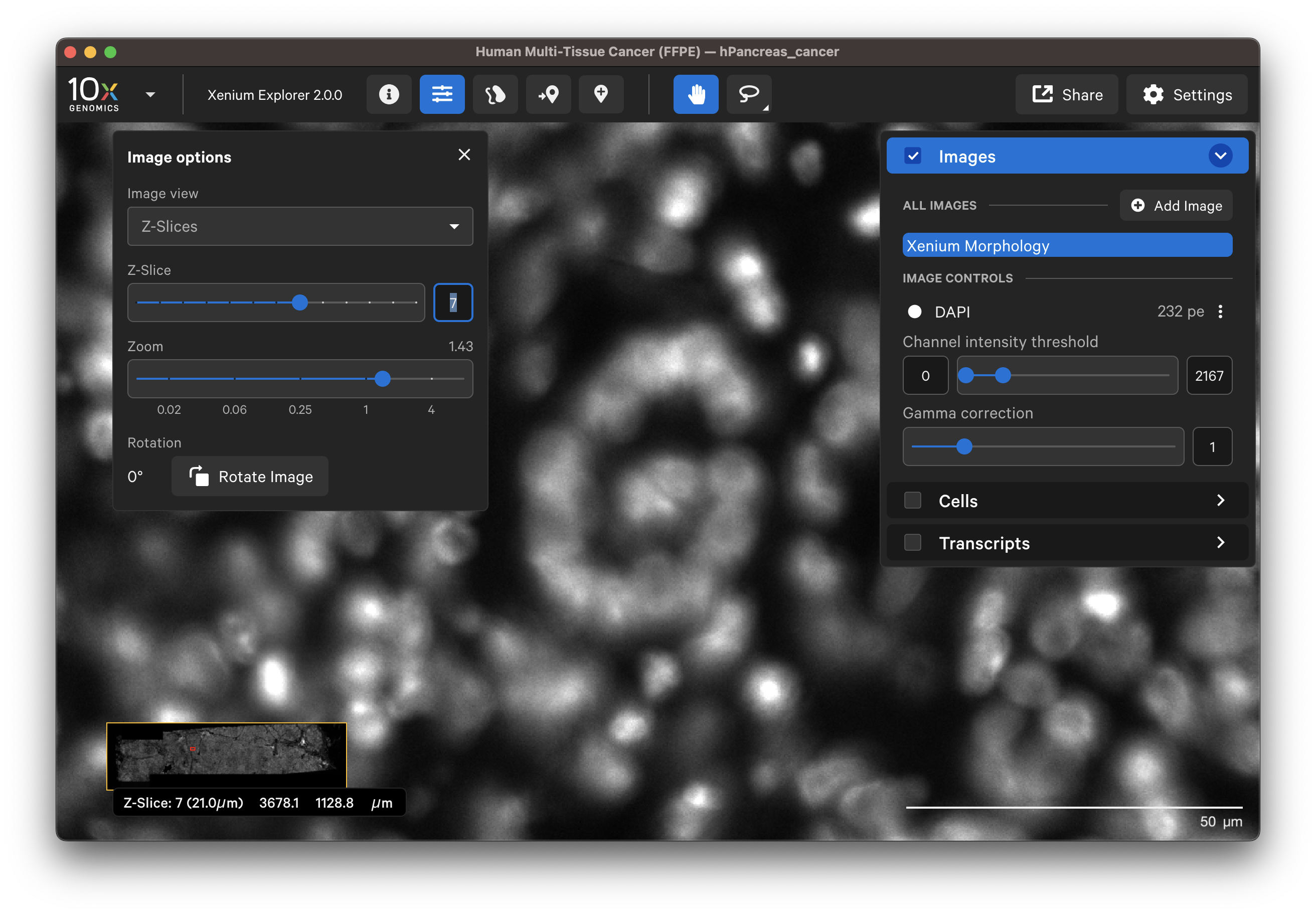
The Autofocus option displays the single best-focus Z-plane from the morphology stain Z-stack morphology_focus/morphology_focus_[xxxx].ome.tif images. The background is minimized in this image. It works best for cells in the tissue that approximate a monolayer, while cells above or below the focal Z-plane may be missed.
- In XOA v2.0 and later, the directory contains the DAPI-stained image, as well as boundary and interior cell images for the multimodal cell segmentation workflow. For multimodal cell segmentation datasets, the DAPI
morphology_focus_0000.ome.tiffile must be present in the directory to load the dataset. To load data without the DAPI image, the OME-XML metadata information must be modified. Python tools such asome-typescan be used to view and modify metadata if needed. - In XOA v1.0 - 1.9, the autofocus output file is called
morphology_focus.ome.tifand it is the DAPI stained image.
This option is only available for data generated in XOA v1.0 - 1.9.
The maximum intensity projection technique converts a 3-dimensional stack of microscope images into a 2-dimensional image. The Maximum Intensity Projection of the DAPI Z-stack morphology_mip.ome.tif image displays the brightest pixel from each layer. All the cells will be visible, however there may be higher background from out-of-focus light.
In Xenium Explorer v2.0 and later, the Images layer loads all morphology channels for multichannel images from multimodal cell segmentation datasets. The channels are labeled by purpose: Nuclear, Boundary, Interior - RNA, and Interior - Protein. Clicking the info icon will switch the labels to the name of the stain(s). Select and layer all channel images to view them simultaneously (Multi Channel) or view one channel at a time (Single Channel).
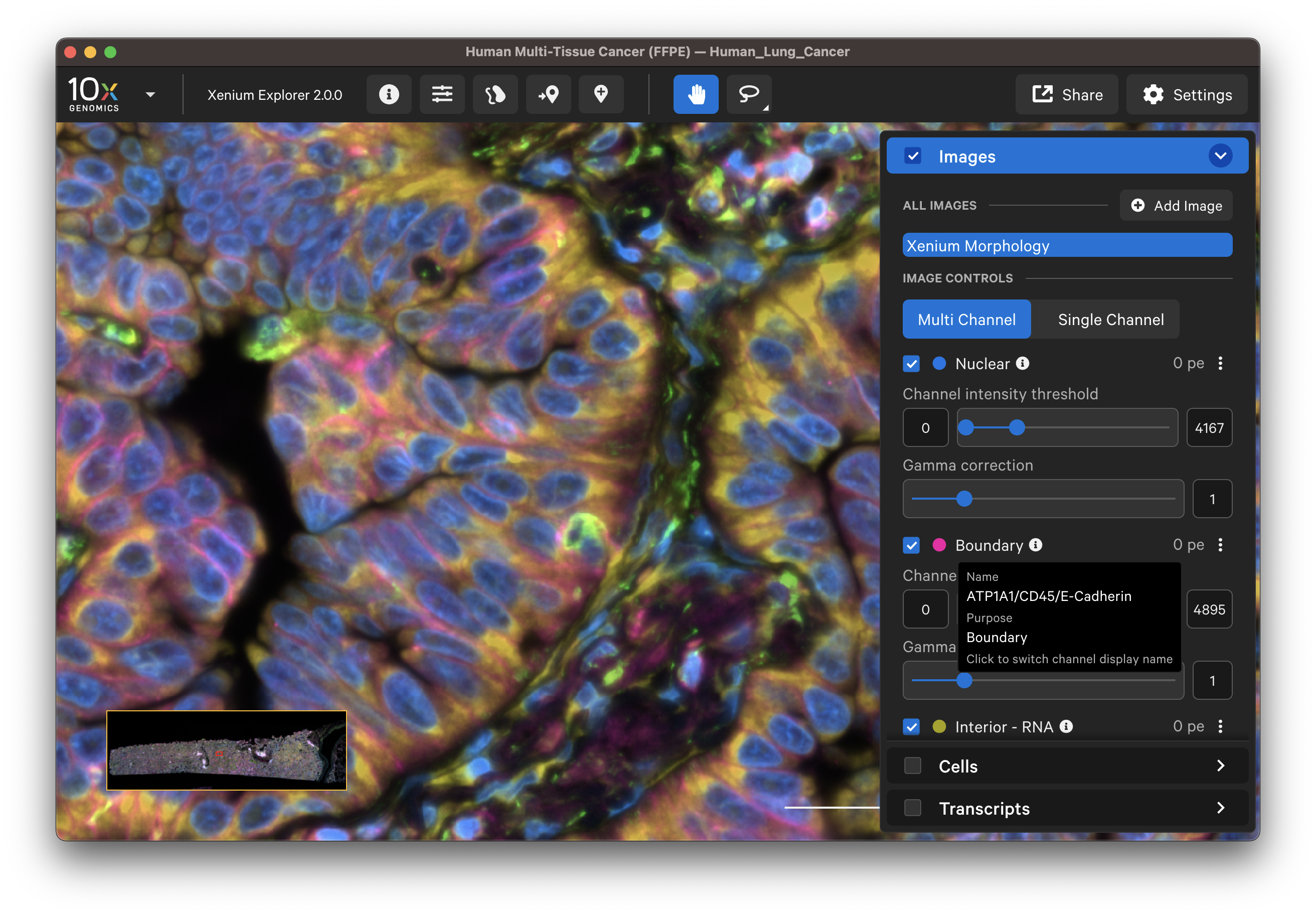
The default channel colors can be changed by clicking on the circle icon. It is also possible to toggle between viewing channels with colors or in grayscale. By default, channel colors are displayed with uniform colors (based on CIELAB color space). This color map is intended to display channel colors with uniform lightness and contrast to evenly distribute multichannel stain signals. When disabled, channels are displayed with a standard color map.
| Uniform colors | Standard colors |
|---|---|
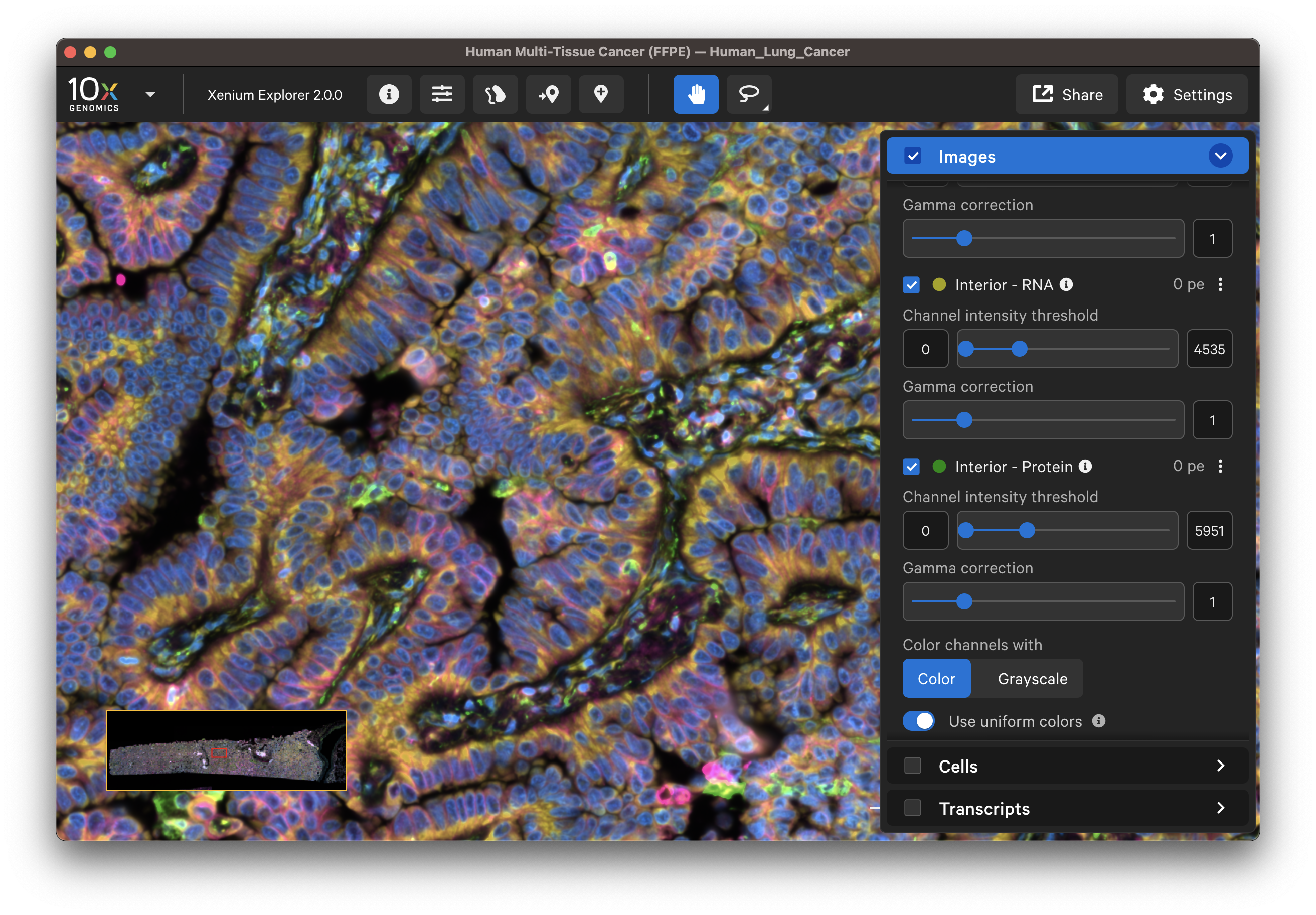 | 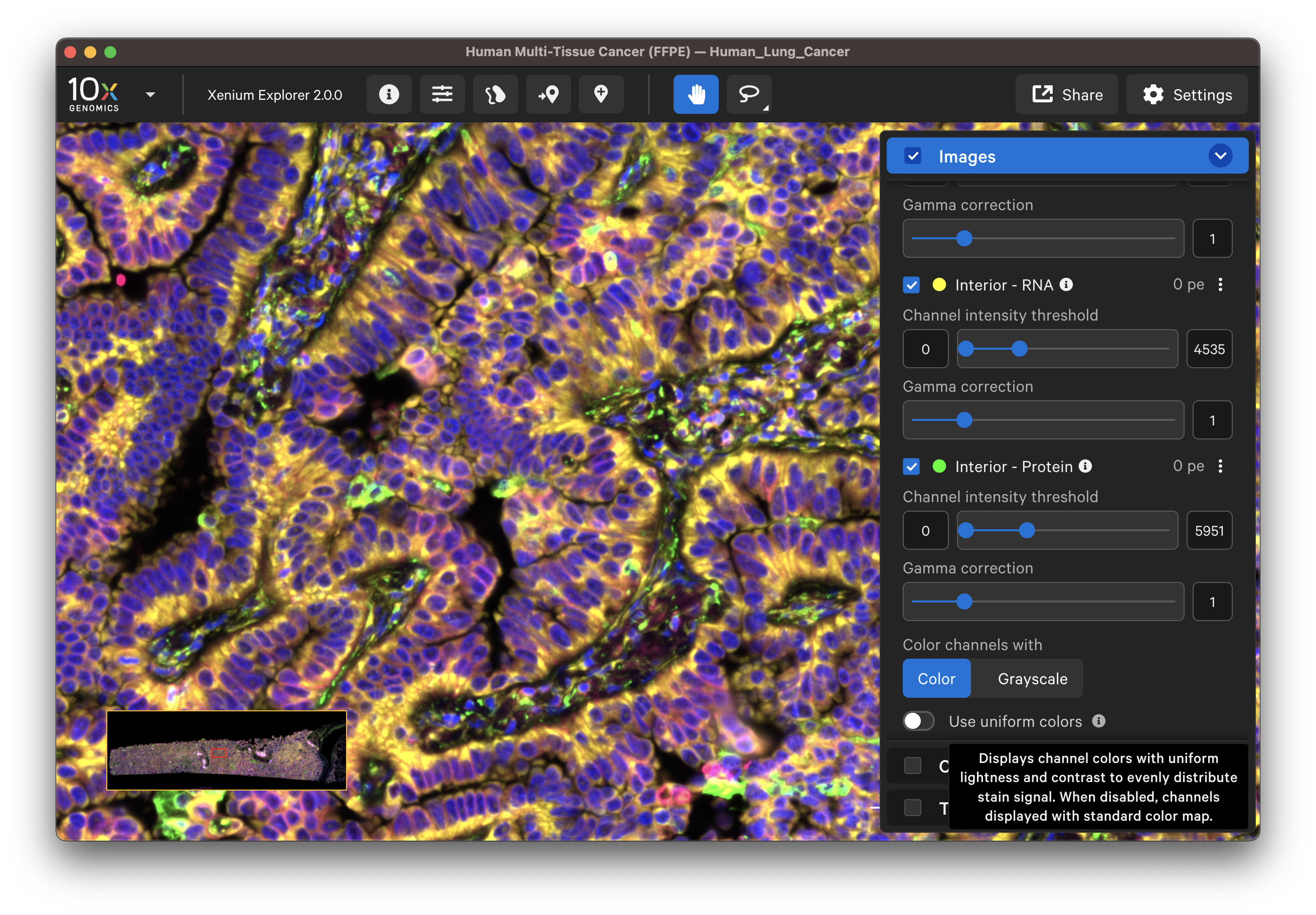 |