There are four primary ways to run Cell Ranger ARC:
- 10x Genomics Cloud Analysis: a scalable platform for data management, analysis, and collaboration to simplify and accelerate the interpretation of data generated from 10x Genomics assays (currently available for customers in the U.S. and Canada only).
- Single Server: Cell Ranger ARC can run directly on a dedicated server. This is the most straightforward approach and the easiest to troubleshoot.
- Job Submission Mode: Cell Ranger ARC can run using a single node on the cluster. Less cluster coordination is required since all work is done on the same node. This method works well even with job schedulers that are not officially supported.
- Cluster Mode: Cell Ranger ARC can run using multiple nodes on the cluster. This method provides high performance, but is difficult to troubleshoot since cluster setup varies among institutions.
Recommendations and requirements, in order of computational speed (left to right):
| Cloud Analysis | Cluster Mode | Job Submission Mode | Single Server | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Recommended for | Default option for users in supported countries | Organizations using an HPC with SGE or LSF for job scheduling | Organizations using an HPC | Users without access to an HPC |
| Compute details | Splits each analysis across multiple compute nodes to decrease run time | Splits each analysis across multiple compute nodes to decrease run time | Runs each analysis on a single compute node | Runs each analysis directly on a dedicated server |
| Requirements | Any laptop or desktop computer | HPC with SGE or LSF for job scheduling | HPC with most job schedulers | Linux computer with minimum 8 cores & 64 GB RAM |
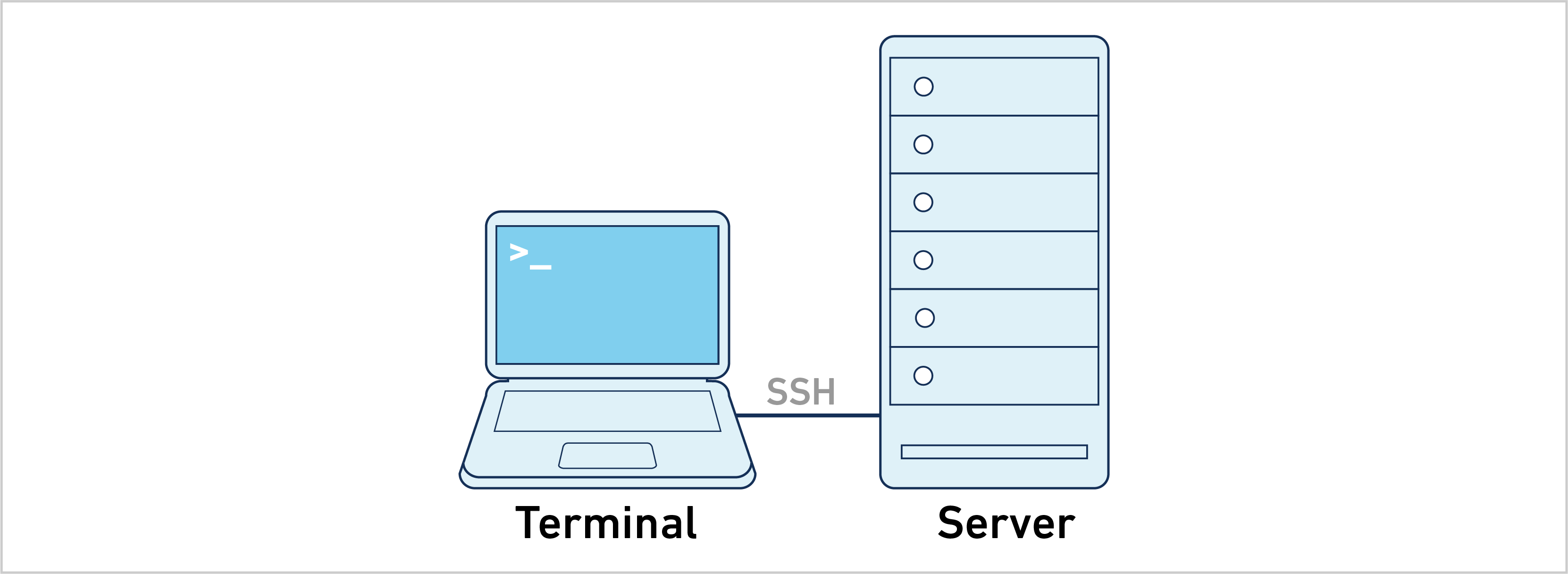
The majority of the information on this website uses the single server approach. Follow the instructions below to analyze a 10x Genomics library:
By default, cellranger-arc uses all available cores and 90% of detected memory. This behavior may be undesirable in a shared environment with multiple concurrent users and tasks. It is strongly recommended to run cellranger-arc with --localcores and --localmem to specify resource usage upper bounds. In practice, there is negligible return in allocating more than 32 cores or 256G to the pipeline. Check the system requirements page for more information on how resource allocations affect pipeline runtime.
Cell Ranger ARC can be run in job submission mode, by treating a single node from the cluster like a local server. This leverages existing institutional hardware for pipeline analysis.
10x Genomics does not officially support Slurm or Torque/PBS. However, many customers have successfully used Cell Ranger ARC with those job schedulers in job submission mode.
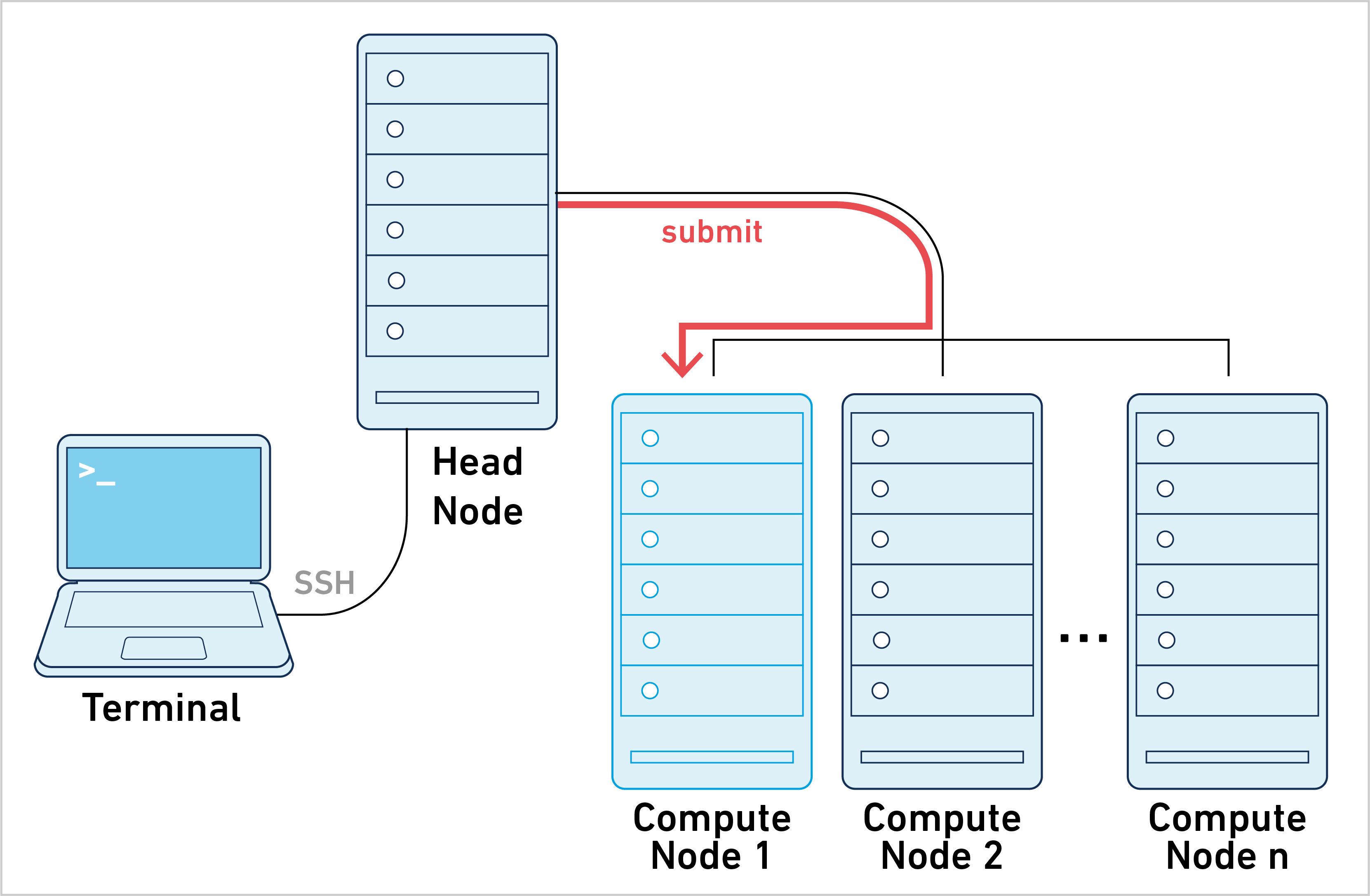
This mode of operation is what most people have in mind when it comes to working with clusters: a large computational job is submitted to the cluster and there is one Job ID to track during job execution. To learn more, please go to the job submission mode page.
Cell Ranger ARC can be run in cluster mode, using SGE or LSF to run the stages on multiple nodes via batch scheduling. This allows highly parallelizable stages to utilize hundreds or thousands of cores concurrently, dramatically reducing time to solution.
10x Genomics does not officially support Slurm or Torque/PBS. However, many customers have successfully used Cell Ranger ARC with those job schedulers in cluster mode, it is unsupported and may require trial and error.
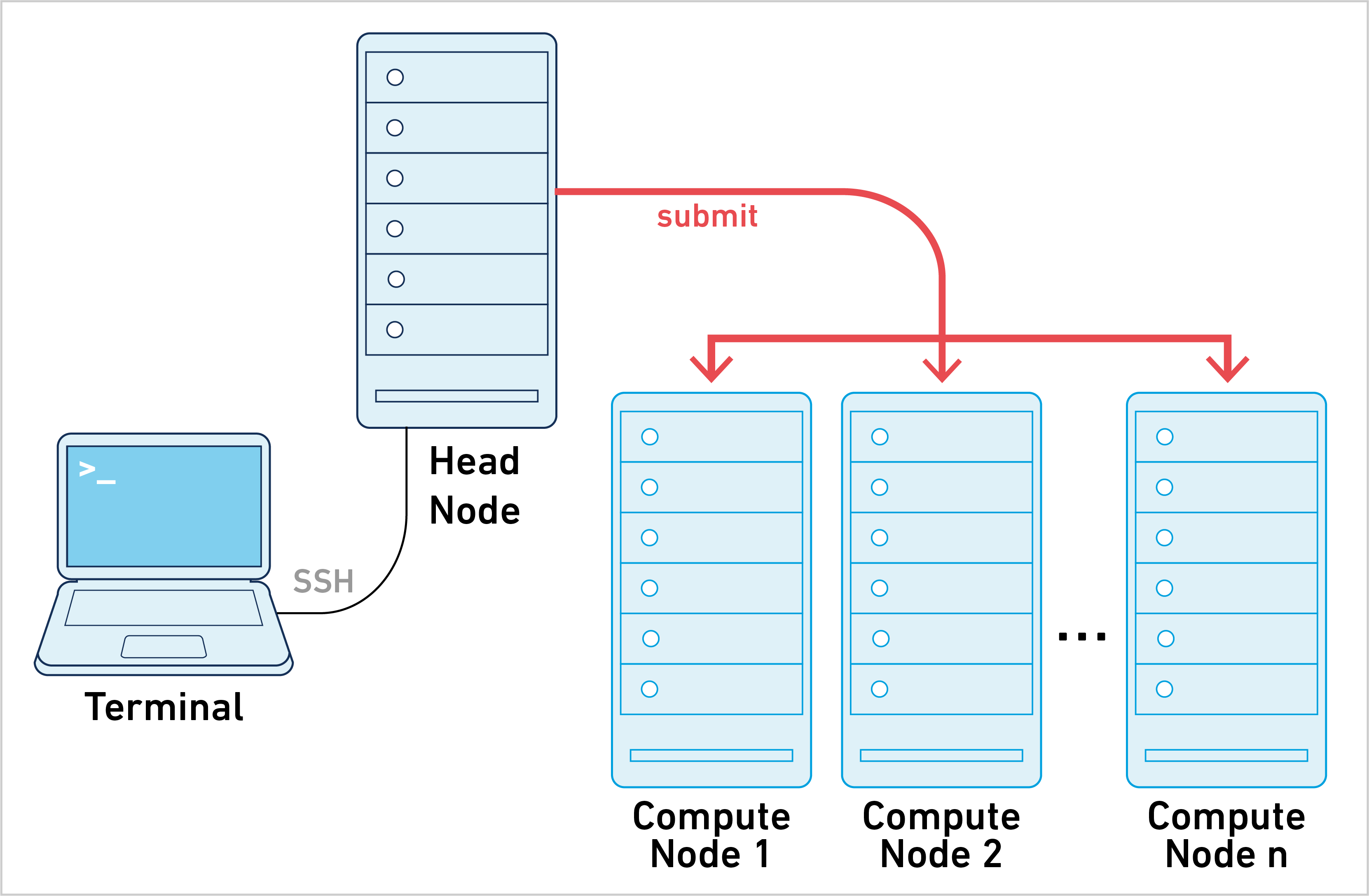
Instead of submitting one job to the cluster, Cell Ranger ARC creates hundreds and potentially thousands of small stage jobs. Each of these stage jobs need to be queued, launched, and tracked by the pipeline framework. The necessary coordination between Cell Ranger ARC and the cluster makes this approach harder to set up and troubleshoot, since every cluster configuration is different. To learn more, please go to the cluster mode page.